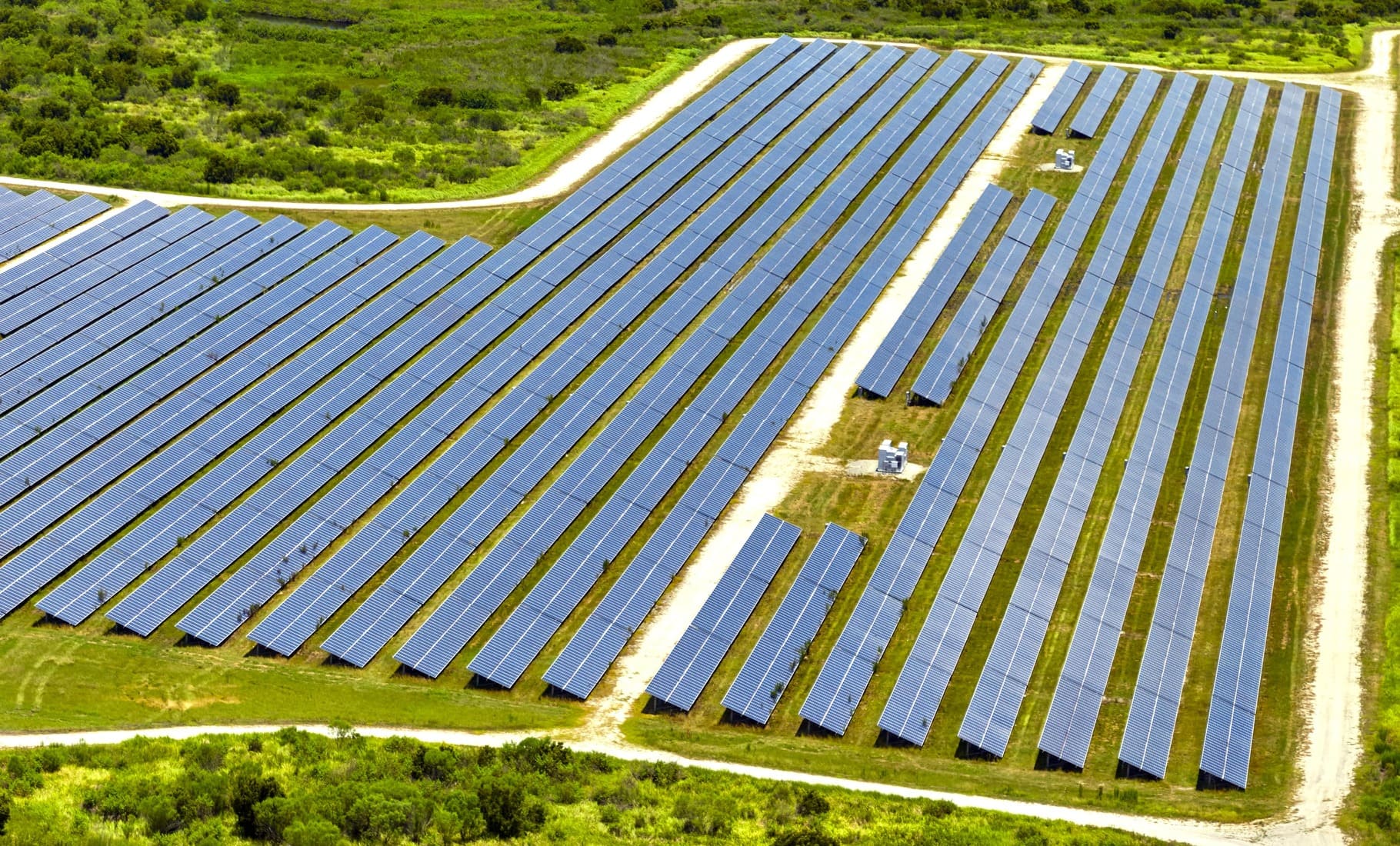
We explore the impact of solar energy on carbon footprint, from panel production to recycling, and highlight key strategies to boost sustainability.
Solar Energy and Carbon Footprint
Today, sustainability and eco-friendly solutions are gaining more importance in the energy sector.
As the world faces climate change and environmental challenges, solar energy has emerged as a key player.
It is considered a clean, limitless, and renewable source of energy—but like any technology, solar energy also has an impact on the carbon footprint.
? Basics of Solar Energy
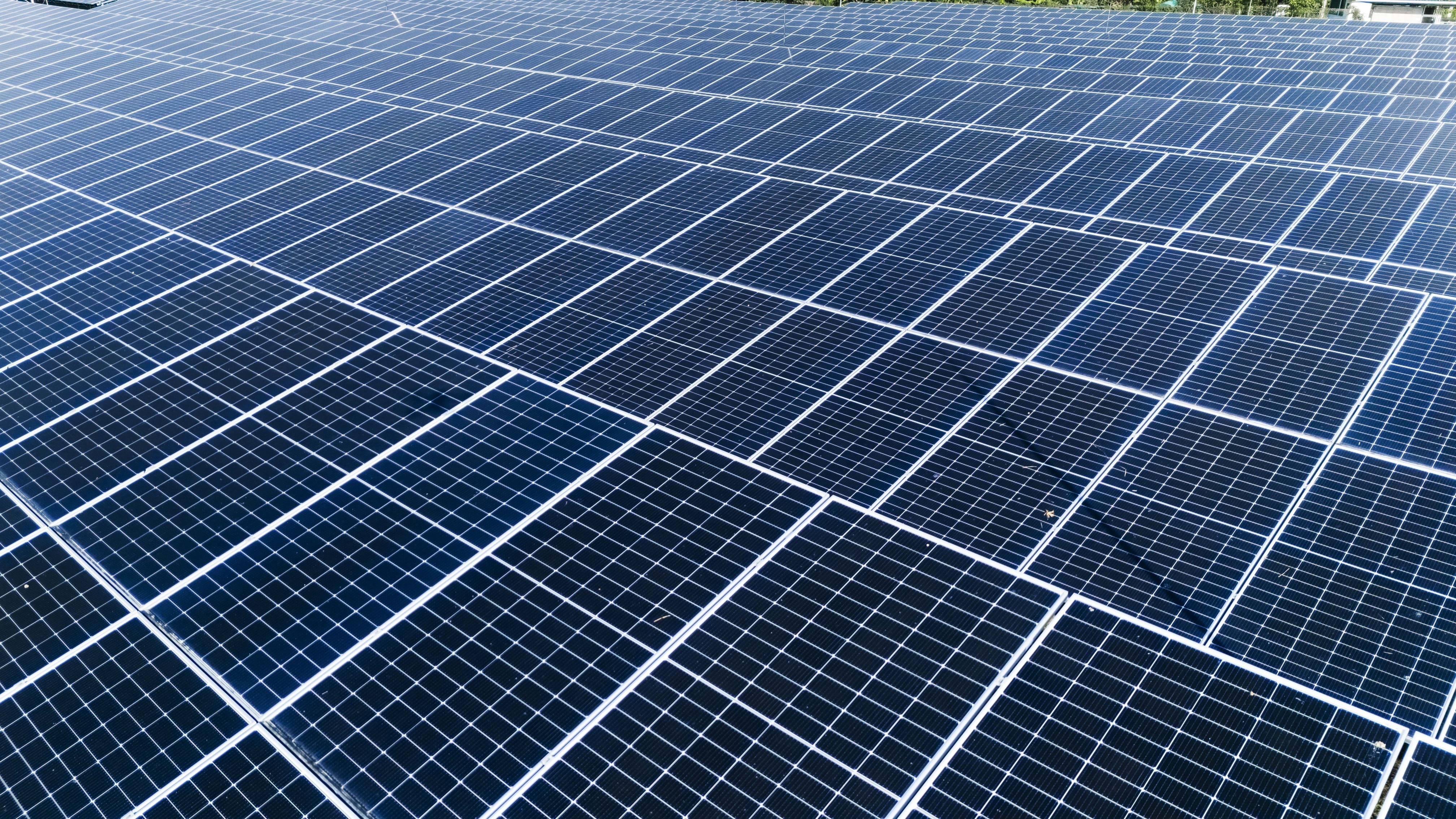
Solar energy is the process of converting sunlight into electricity or heat energy.
It is mainly used through two methods:
• Thermal Solar Energy: Sunlight is converted into heat energy to heat water or produce steam, which can then generate electricity via turbines.
• Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Energy: Solar rays are directly converted into electricity using photovoltaic cells that absorb sunlight and generate electric current.
Solar energy systems require minimal maintenance, emit no harmful gases during use, and significantly reduce energy costs in the long term.
? Impact of Solar Energy on Carbon Footprint
While solar energy is nearly emission-free during operation, its production and disposal stages contribute to its overall carbon footprint.
• Manufacturing PV panels involves materials like silicon, which require high temperatures and chemical processes—leading to CO₂ emissions.
• End-of-life panel recycling also consumes energy and produces emissions depending on how materials are handled.
✅ Sustainability Potential of Solar Energy
Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy produces no carbon emissions during usage, making it a clean and sustainable option for the future.
• Requires less maintenance
• Long lifespan and high efficiency
• Minimizes greenhouse gas emissions
• Helps reduce dependency on fossil fuels
? How to Further Reduce Solar Energy's Carbon Footprint
1. Clean Energy Generation: Widespread use of solar energy replaces fossil fuels, cutting down CO₂ emissions significantly.
2. Energy Storage Solutions: Better energy storage allows solar power to be used at night or on cloudy days—reducing reliance on carbon-heavy sources.
3. Panel Recycling: Efficient recycling helps recover valuable materials and reduce environmental impact at the end of the panel's life.
4. Technology Advancements: More efficient panels and manufacturing processes mean less energy used and lower emissions overall.
5. Awareness and Education: Conscious use and better understanding of solar energy increase efficiency and support sustainability goals.
? Conclusion:
With low emissions and limitless potential, solar energy is one of the most important tools in the transition to clean, sustainable energy systems.
Through responsible production, smart design, and proper end-of-life handling, solar power’s carbon footprint can be reduced even further.
The future of energy lies not just in how we produce it—but in how responsibly we do it. Solar energy is leading this transformation.
As the world faces climate change and environmental challenges, solar energy has emerged as a key player.
It is considered a clean, limitless, and renewable source of energy—but like any technology, solar energy also has an impact on the carbon footprint.
? Basics of Solar Energy
Solar energy is the process of converting sunlight into electricity or heat energy.
It is mainly used through two methods:
• Thermal Solar Energy: Sunlight is converted into heat energy to heat water or produce steam, which can then generate electricity via turbines.
• Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Energy: Solar rays are directly converted into electricity using photovoltaic cells that absorb sunlight and generate electric current.
Solar energy systems require minimal maintenance, emit no harmful gases during use, and significantly reduce energy costs in the long term.
? Impact of Solar Energy on Carbon Footprint
While solar energy is nearly emission-free during operation, its production and disposal stages contribute to its overall carbon footprint.
• Manufacturing PV panels involves materials like silicon, which require high temperatures and chemical processes—leading to CO₂ emissions.
• End-of-life panel recycling also consumes energy and produces emissions depending on how materials are handled.
✅ Sustainability Potential of Solar Energy
Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy produces no carbon emissions during usage, making it a clean and sustainable option for the future.
• Requires less maintenance
• Long lifespan and high efficiency
• Minimizes greenhouse gas emissions
• Helps reduce dependency on fossil fuels
? How to Further Reduce Solar Energy's Carbon Footprint
1. Clean Energy Generation: Widespread use of solar energy replaces fossil fuels, cutting down CO₂ emissions significantly.
2. Energy Storage Solutions: Better energy storage allows solar power to be used at night or on cloudy days—reducing reliance on carbon-heavy sources.
3. Panel Recycling: Efficient recycling helps recover valuable materials and reduce environmental impact at the end of the panel's life.
4. Technology Advancements: More efficient panels and manufacturing processes mean less energy used and lower emissions overall.
5. Awareness and Education: Conscious use and better understanding of solar energy increase efficiency and support sustainability goals.
? Conclusion:
With low emissions and limitless potential, solar energy is one of the most important tools in the transition to clean, sustainable energy systems.
Through responsible production, smart design, and proper end-of-life handling, solar power’s carbon footprint can be reduced even further.
The future of energy lies not just in how we produce it—but in how responsibly we do it. Solar energy is leading this transformation.